Fair Weather Forecasting? The Shortcomings of Big Data for Sustainable Development, a Case Study from Hubballi-Dharwad, India
Abstract
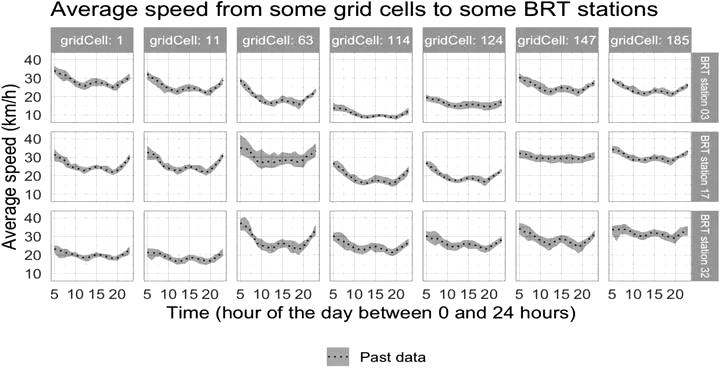
Sustainable urban mobility is an essential component of sustainable development but requires careful planning in rapidly growing urban areas. This paper investigates the value and limitations of Big Data for evaluating transport policies, plans, and projects in Hubballi-Dharwad, India. Results show how Big Data can enable the outcomes of transport interventions to be evaluated more readily than conventional transport analysis. However, the analysis also found that this data may be less able to detect the impacts of travel behaviours in informal settlements, and the impact of extreme weather events. These potential shortcomings, as well as a lack of transparency around the methodology and data sources used by sources of Big Data, could generate unintended consequences and biases in transport planning. Reflecting on these challenges, and the wider implications for urban governance, we conclude that there is an urgent need for Big Data and other technical advances in urban modelling to be seen as compliments to, rather than substitutes for, wider methods of knowledge generation in urban areas.